Malaysia’s ambition to become a high-income, digital-first nation is clear in the MADANI Economy framework. Recent discussions on investor-friendly policies and legislation to support Artificial Intelligence (AI) development further highlight the commitment to fostering a thriving digital economy.
To realise this ambition, it is crucial to harness the potential of AI and related technologies. The transformative potential of AI in Malaysia’s economic landscape is substantial.
AI’s influence is notably strong in Malaysia’s dominant sectors: manufacturing and consumer-facing services like retail and hospitality. Manufacturing, representing nearly a quarter of the GDP in 2023, stands to gain the most. AI can enhance productivity and streamline operations, for instance, by shifting from predictive maintenance (relying on IoT sensor devices and data to predict when assets will require maintenance) to prescriptive maintenance (using AI tools to analyse equipment data for targeted risk-reduction strategies).
AI is also transforming the way businesses interact with customers. In the hospitality sector, the Malaysia Budget & Business Hotel Association (MyBHA) is partnering with hospitality technology solutions provider Vendfun to implement AI-powered guest services and resource management in hotels across the country. Meanwhile, in the retail industry, Malaysian startups like Retailetics are pioneering AI-powered shopping carts, such as the ezyCart, which simplifies product location and checkout processes. The potential for AI adoption in retail is substantial, with smart retail revenue projected to soar past USD25 billion by 2025, a significant jump from just over USD8 billion in 2020. This dramatic increase underscores the vast opportunities for AI implementation across similar applications, promising a future where AI-powered solutions become an integral part of the consumer experience.
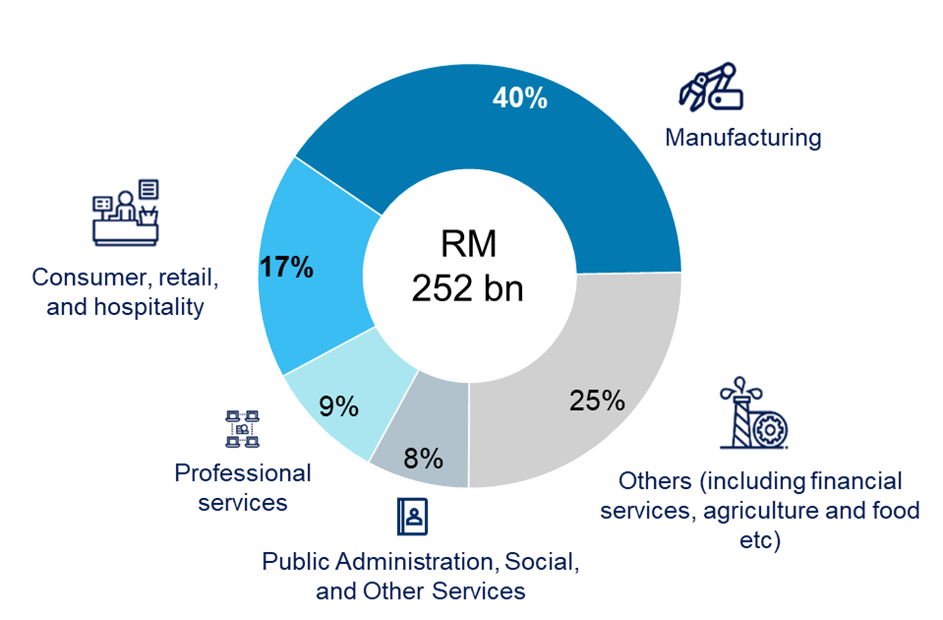

Breakdown of potential annual economic benefits from AI-enabled technologies, by sector (%, 2030)
Malaysia is well-placed to tap Southeast Asia’s 2030 AI opportunity. We estimate that RM252 billion (USD 55 billion) of economic benefits are expected for Malaysian businesses in 2030,[1] if AI-powered products and solutions are adopted, as we have seen in the manufacturing and retail sectors thus far. This represents a significant opportunity for Malaysia, equivalent to 9% of its projected 2030 GDP and 11% of the total AI potential in key Southeast Asian markets.
RM252 billion (USD 55 billion) of economic benefits are expected for Malaysian businesses in 2030, if AI-powered products and solutions are adopted.
The imperative for an AI-ready workforce
Fully realising the opportunity AI provides hinges on addressing the critical skills gap in the workforce. The Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC) reported that Q1 2024 saw sharp increases in the demand for digital talents, particularly in industries such as IT systems design and engineering services, which saw a growth of over 200%.
Bridging the skills gap through targeted initiatives, such as job platforms and training programs, is not just an educational imperative; it is an economic one. Our estimates suggest that narrowing the digital skills gap could unlock RM88 billion (USD 19 billion) in annual GDP for Malaysia in 2030. In essence, equipping the workforce with the digital skills needed to adapt to the evolving technological landscape, such as the use of prompt engineering, data analytics, and UX design, is key to ensuring Malaysia fully capitalises on the AI opportunity.
RM88 billion (USD 19 billion) of annual GDP in Malaysia can be added in 2030 by narrowing the digital skills gap through digital skills training and greater adoption of education technologies.
AI is creating a significant shift in the composition of jobs across industries, creating an opportunity for workers to upskill and focus on more complex tasks, leading to a more competitive labour market. For instance, in manufacturing, AI-driven predictive maintenance can help identify potential equipment failures before they occur. In the retail sector, AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to provide more personalised assistance. Investing in AI skills training will be key for Malaysia to capitalise on this opportunity and thrive in the AI-driven economy.
Keeping Malaysia’s AI future safe and secure
Robust cybersecurity is required to build a secure infrastructure for AI innovation and adoption. Cybersecurity is a key concern for Malaysia, which continues to grapple with the increasing threat of cybercrime, ranking as the 8th most breached country globally in 2023.
While we must acknowledge the potential for AI to be used for harmful purposes, it is also emerging as a critical ally. Globally, more than 40% of people view better security as a top application for AI—and our research shows AI’s potential economic impact in preventing cybercrime for Malaysian businesses:
RM48 billion (USD 11 billion) in cybercrime losses could be prevented in 2030 if businesses deploy AI-powered cybersecurity capabilities.
These findings underscore the multifaceted impact of AI in shaping Malaysia’s future. It is not just an economic catalyst, but also a tool for empowering the workforce and safeguarding against digital threats.
Google’s economic impact in Malaysia
Google has been partnering with Malaysia on its journey to tap the economic opportunity from AI and other digital technologies. Through AI-powered products and solutions, such as Google Search and Google Ads, Malaysian businesses are expanding their online presence both locally and globally. Additionally, Google Cloud provides AI, infrastructure, developer, data, security, and collaboration tools to businesses of all sizes to help them boost cost efficiency, enhance collaboration and productivity, and innovate and scale to reach new users.
In 2023, Google Search, Google Ads, Google AdSense, Google Play, Google Cloud, and YouTube helped provide RM15 billion (USD 3.3 billion) of economic activity for businesses.
This represents a 15% increase from the previous year, highlighting the growing role of Google’s products and services in fueling Malaysia’s digital economy.
The growth of businesses translates into increased hiring. In 2023, Google’s products and services supported about 52,000 jobs in the Malaysian economy, with an additional 59,900 jobs generated through the vibrant Android app ecosystem.
Google is also helping to equip Malaysians with in-demand digital skills. The recently launched Google AI Essentials course empowers people from any background to gain essential AI skills. This self-paced program, taught by Google’s AI experts, uses practical examples on how AI can boost productivity and be helpful for everyone.
Beyond businesses, Google’s AI-powered products, like the Gemini app and Google Search, are making AI accessible and information readily available to Malaysian households. Other AI-powered tools such as Google Maps, Google Drive, and Google Photos enable greater productivity and convenience in daily life. Moreover, YouTube and Google Play offer a diverse range of educational and entertainment content, further enriching the lives of Malaysians.
Looking ahead, Google’s commitment to Malaysia’s digital future is further underscored by its significant investments in the country. In 2024, Google is making its largest planned investment in Malaysia worth USD2 billion, including the development of its first Google data centre and Google Cloud region to meet the growing demand for cloud services. Building on Google’s partnership with the Government of Malaysia to advance its Cloud First Policy, the upcoming Google Cloud region will make it easier and faster for traditional enterprises, small and medium-sized businesses, and start-ups alike to access Google Cloud’s on-demand capabilities. These resources are faster, more reliable, and offer superior economics compared to building their own infrastructure. Additionally, the new Cloud region will provide customers with more choices for local data storage, enabling them to keep sensitive data within borders and meet security requirements.
- RM14 billion (USD 3.2 billion) of contribution to GDP will be generated by the new Google Cloud region by 2030.[2]
- 26,500 full-time equivalent jobs such as cloud engineers and data scientists will be created through the Google Cloud region in 2030.
- 78% improvement in energy efficiency could be achieved through the migration of on-premise data centres to cloud, enabling organisations to reduce energy consumption and associated emissions.
Google’s ongoing investment in supporting Malaysian businesses and households through its diverse range of products and services positions it as a key partner in the country’s digital transformation journey.
We use a consistent methodology year-over-year for annual estimations of Google’s economic impact in Malaysia, and for projecting the economic benefits of digital skills and cybersecurity in 2030. The 2030 projections remain fixed, while Google’s impact estimates are updated yearly with the same methodology. Detailed methodology information is provided below.
Important information:
This post has been prepared by Access Partnership for Google. All information in this post is derived or estimated by Access Partnership analysis using both non-Google proprietary and publicly available information. Google has not supplied any additional data, nor does it endorse any estimates made in this post.
Note: All calculations were done in USD and converted to RM based on the average exchange rate in 2023 of 1 USD = 4.56 MYR, obtained from the IMF database, unless otherwise mentioned.
[1] The economic benefits of AI in 2030 were assessed by conducting a sector-specific analysis of the impacts of both traditional and generative AI within each sector. This evaluation involved measuring the sector-targeted effects of over 400 traditional AI applications and over 60 use cases related to generative AI.
[2] This estimate was computed in 2022 in USD and converted to RM based on the average exchange rate in 2022 of 1 USD = 4.40 MYR, obtained from the IMF database.


Authors